DNA profile can determine the gender of a person by simply testing their DNA. Although we are very unique in different ways, our DNA is very similiar to other people's DNA.
How can you create a DNA profile? It's simple, just follow the steps below and you can create your own DNA profile. The first method is called RFLP, restriction fragment length polymorphism. Today, this method is not commonly use because it requires a large sample of DNA and multiple sections of the DNA strand.
1. You first have to get a sample of DNA. DNA can be found anywhere in your body. You can even get a sample of DNA from a person by using a mouth swab to get the inner cheek cells from a body.
2. Then you extract the DNA nuclei from the white blood cells that you separated from the red and white blood cells. The way you have to do it, is to bathe the cells in hot water with salt in it and then put it back into the centrifuge.
3. Next, you cut DNA stand into the fragments that is using a restriction enzyme. Make sure you carefully cut it.
4. Next, put fragments in one of the end of the agarose gel, which is a type of a seaweed that turns into gelatin once it is dissolved in boiling water.
5. Then place the agarose gel into the gel electrophoresis apparatus that will use electric current to separate DNA segments by length.
6. Finally, use a sheet of nitrocellulose or nylon to blot the DNA. This paper is stained so you can see the different lengths of DNA bands with your naked eyes.
Picture of RFLP Process
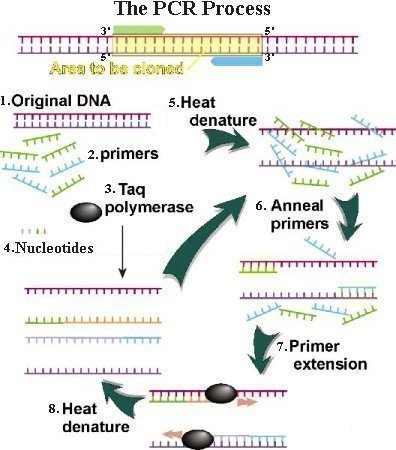
The more prevalent method used by Scientist today is PCR, polymerase chain reaction. This method requires a small amount of DNA sample and it will produce replicates of DNA sequences. Here are the steps of PCR.
1. Find a DNA sample that is suitable for testing.
2. Next, use the Taq polymerase to add nucleotide on to the new stand. Taq polymerase is a heat-stable enzyme separated from the bacterium.
3. The sample needs to be heated to a temperature up to 98 degrees Celsius in order for the double helix DNA strands to separate. This process is called denaturation.
4. You then want to cool down the sample and while that is processing, the synthesis primers will anneal to its complimentary site on the DNA strands.
5. The Taq polymerase will then add complimentary nucleotides to the DNA strand to elongate the synthesis strand starting at the primer site. The end result will be two daughter double helix DNA.
6. The cycle repeats with denaturation, primer annealing and strand elongation of the double helix DNA.
7. The new DNA that carries the long single-stranded tail will make billions of copies by the 30th cycle.